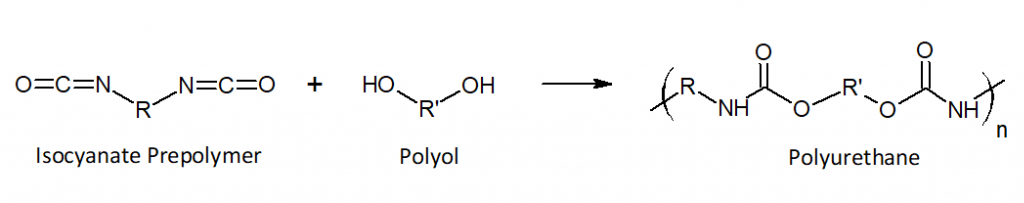
1.What Is Polyurethane?
Polyurethane is a synthetic material that was first developed by German chemist Otto Bayer during the late 1930s. It’s comprised of organic compounds that are connected with carbamate links. Also known as urethane links, the carbamate links play an important role in the properties of polyurethane, as they affect the material’s level of flexibility and elasticity. Manufacturing companies can alter the physical properties of polyurethane — and therefore products containing polyurethane — by using different types of carbamate links.
from:https://matmatch.com/learn/material/polyurethane
2.Properties of polyurethane
Polyurethane typically lasts longer than rubber, especially in applications where it’s constantly stretched or otherwise exposed to stress. Both rubber and polyurethane are elastic and flexible. Polyurethane, however, can withstand significantly more cycles of repeated stretching than its counterpart because of its carbamate links. When used in the production of automotive components, polyurethane can often last for the lifespan of the vehicle. Rubber is also long-lasting, but it’s prone to degradation from repeated stretching or stress.
from:https://monroeengineering.com/blog/polyurethane-vs-rubber-whats-the-difference/
| Properties | Thermoplastic Polyurethane |
| Density | 0.05 – 1.7 g/cm3 |
| Elastic Modulus | 0.03 – 1.88 GPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 0.029 – 18 GPa |
| Elongation at Break | 2 – 950% |
| Hardness | 45-98 Shore A51-85 Shore D |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 100-200 10-6 /ºC |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.14 – 0.5 W/m.K |
| Max. Service Temperature | 80 – 90°C (120-135°C short-term) |
| Min. Service Temperature | ~ -60°C |
| Dielectric Strength | 17-25 kV/mm |
from:https://matmatch.com/learn/material/polyurethane
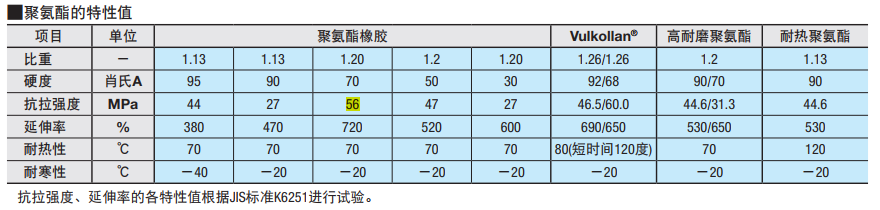
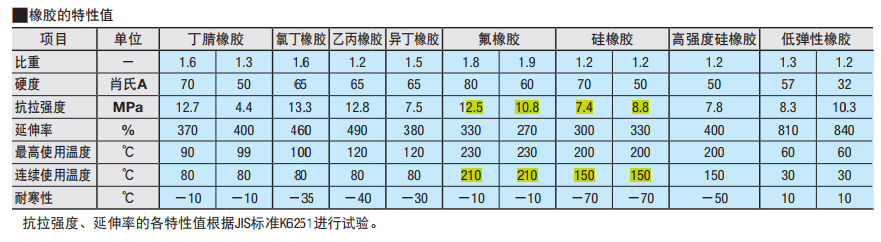
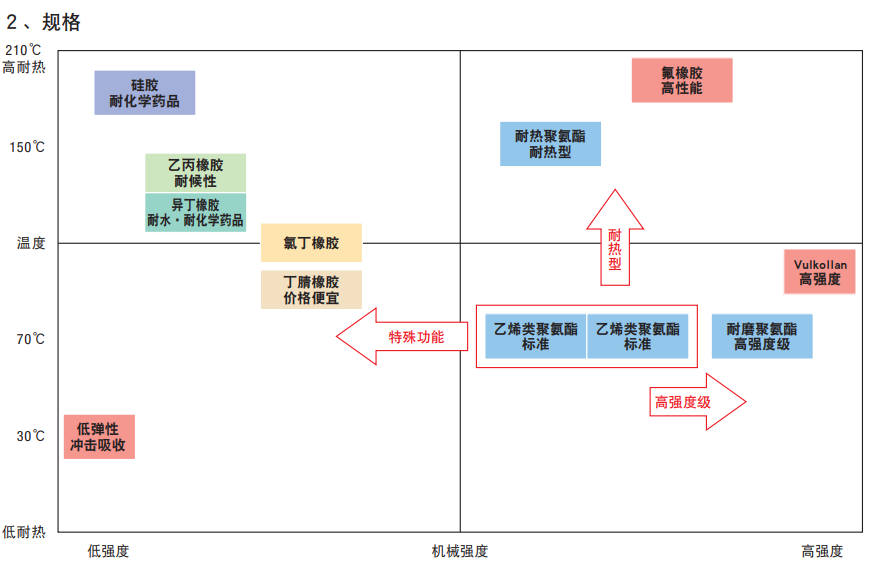
3.Comparation Between Polyurethane and Rubber

4.Uses of polyurethanes
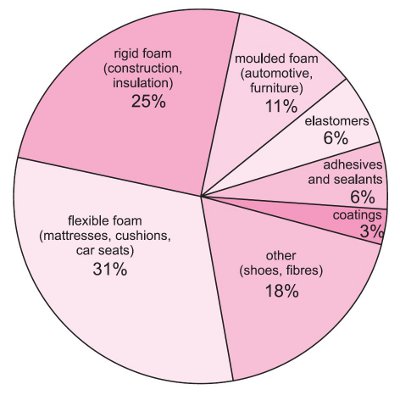
Some examples of the main reasons for choosing polyurethanes as shown in Table 1.
| Uses | Reasons |
|---|---|
| cushioning(缓冲) | low density, flexibility, resistance to fatigue(低密度,弹性,耐疲劳) |
| shoe soles(鞋底) | flexibility, resistance to abrasion, strength, durability(弹性好,耐磨,强度好,耐久性好) |
| building panels(建筑板) | thermal insulation, strength, long life(热绝缘,强度高,寿命长) |
| artificial heart valves(人造心脏瓣膜) | flexibility and biostability(生物稳定性) |
| electrical equipment(电气设备) | electrical insulation, toughness, resistance to oils(绝缘,韧性好,耐油) |
from:https://www.essentialchemicalindustry.org/polymers/polyurethane.html
Flexible Polyurethane Foam
Flexible polyurethane foam is light, durable, supportive and comfortable. It is commonly used for cushioning in bedding, furniture, automotive interiors, carpet underlay and packaging. This accounts for 30% of the polyurethane market due to its commodity usage


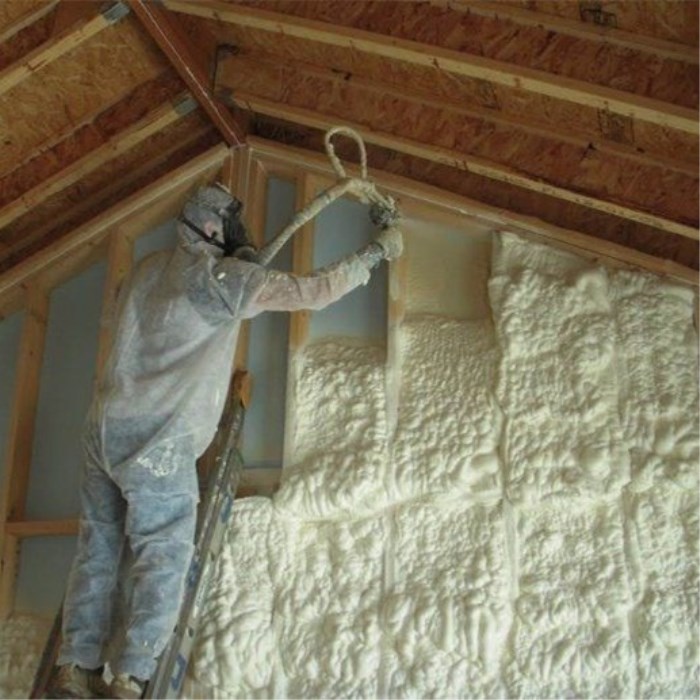
Rigid Polyurethane Foam
Rigid polyurethane foams are the most economic and energy-efficient insulations, significantly cutting energy costs. When used in roof and wall insulation, insulated windows and doors, it helps maintain a uniform temperature and reduce noise levels. Rigid polyurethane foam is also commonly used as thermal insulation in refrigerators and freezers.
Elastomers
Polyurethane elastomers are used in a very wide range of applications, essentially in the engineering field, where properties of durability, abrasion resistance and chemical and oil resistance are needed. Applications include rollers and belts to carry minerals in quarrying operations, wheels for Rollerblades and hospital trolleys, rollers for printing processes and hoses, and other components in under-the-bonnet automotive applications.
from:https://www.polyurethanes.org/en/where-is-it/other-applications/
Sealants
Sealants prevent liquids and heat from entering or escaping through gaps and crevices. Polyurethanes are tough and can be used in harsh climatic conditions to protect windows. Sealants help to reduce heat loss, decreasing energy bills and carbon footprints. Other sealant applications include concrete expansion joints in the construction sector and pre-formed gasket seals in the automotive sector. Sealants are also used in electrical and electronic equipment to stop moisture entering components such as joints and switchgear devices.
Adhesives
Polyurethanes are so versatile that they are also available in the form of glues that can safely bind together quite different materials, such as wood, rubber, cardboard or glass.

Coatings
Many modern coatings, whether for vehicles and cables, floors and walls, or bridges and roads, contain polyurethanes, which safely and effectively shield exposed surfaces from the elements and various forms of pollution, so that they look better and last longer.
The durability, corrosion resistance and weather resistance of polyurethanes makes them suitable for coating all kinds of surfaces. Applications range from concrete constructions like bridges and motorway structures, to steel railway carriages and wooden furniture.
国内厂商:
江苏美思德化学股份有限公司http://www.maysta.com/about/about.aspx








留言