1.What is fuel cell?
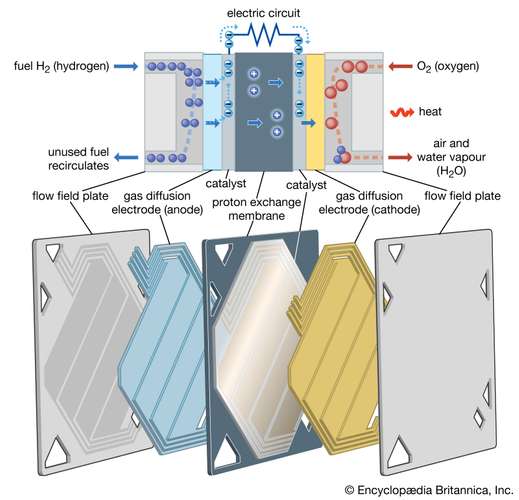
A fuel cell consists of two electrodes—a negative electrode (or anode) and a positive electrode (or cathode)—sandwiched around an electrolyte. A fuel, such as hydrogen, is fed to the anode, and air is fed to the cathode. In a hydrogen fuel cell, a catalyst at the anode separates hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons, which take different paths to the cathode. The electrons go through an external circuit, creating a flow of electricity. The protons migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they unite with oxygen and the electrons to produce water and heat.
来自 <https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/fuel-cells>
2.Why do people intend to develop the technology?

The fuel cell can supply electrical energy over a much longer period of time. This is because a fuel cell is continuously supplied with fuel and air (or oxygen) from an external source, whereas a battery contains only a limited amount of fuel material and oxidant that are depleted with use.
来自 <https://www.britannica.com/technology/fuel-cell>
The fuel cell converts chemical energy directly into electrical energy. Because of this fundamental characteristic, fuel cells may convert fuels to useful energy at an efficiency as high as 60 percent, whereas the internal-combustion engine is limited to efficiencies near 40 percent or less.
来自 <https://www.britannica.com/technology/fuel-cell>
They also emit no noxious gases such as nitrogen dioxide and produce virtually no noise during operation, making them contenders for local municipal power-generation stations.
来自 <https://www.britannica.com/technology/fuel-cell>
3.What is the barrier of using the Fuel cell?
While the technology has proven to be workable, efforts to make it commercially competitive have been less successful because of concern with the explosive power of hydrogen, the relatively low energy density of hydrogen, and the high cost of platinum catalysts used to create an electric current by separating electrons from hydrogen atoms.
来自 <https://www.britannica.com/technology/fuel-cell>
Cost, performance, and durability are still key challenges in the fuel cell industry.
来自 <https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/fuel-cells>
4.Applications of fuel cell



5.Further reading
6 questions about hydrogen fuel cell cars: you’re just a click away from the answers





留言