Mostly from:https://www.britannica.com/science/solar-energy
1.What is solar energy?
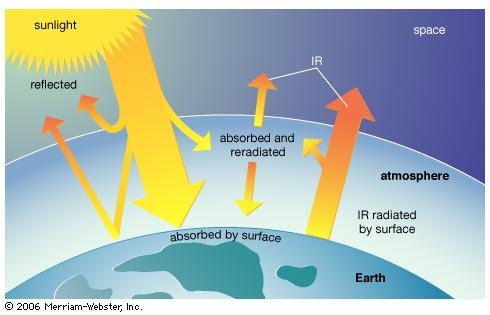
The sunlight that reaches the ground consists of nearly 50 percent visible light, 45 percent infrared radiation, and smaller amounts of ultraviolet and other forms of electromagnetic radiation.
The potential for solar energy is enormous, since about 200,000 times the world’s total daily electric-generating capacity is received by Earth every day in the form of solar energy.
2.Problem we met in using it?
Intensity at Earth’s surface is actually quite low. Though solar energy itself is free, the high cost of its collection, conversion, and storage still limits its exploitation in many places.
3.How do we use solar energy currently?
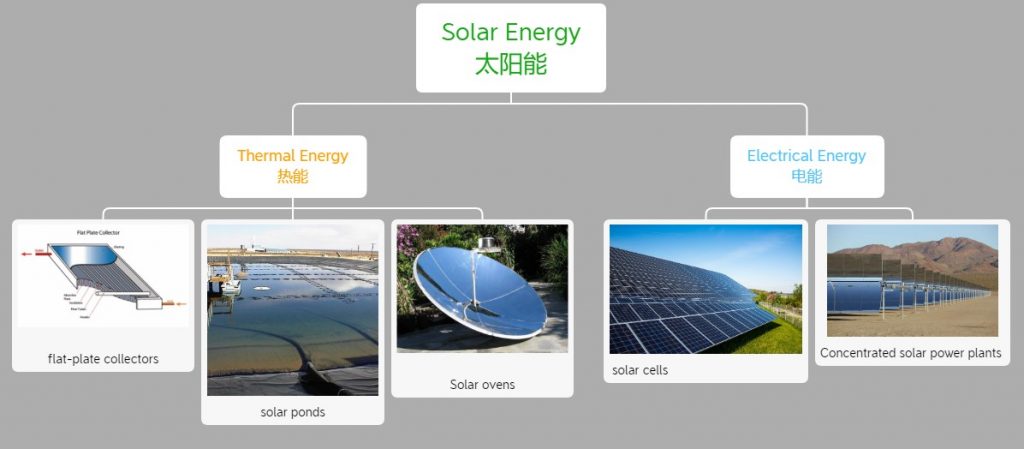
Flat-plate collectors:
The flat-plate solar collectors are probably the most fundamental and most studied technology for solar-powered domestic hot water systems. The overall idea behind this technology is pretty simple. The Sun heats a dark flat surface, which collect as much energy as possible, and then the energy is transferred to water, air, or other fluid for further use.
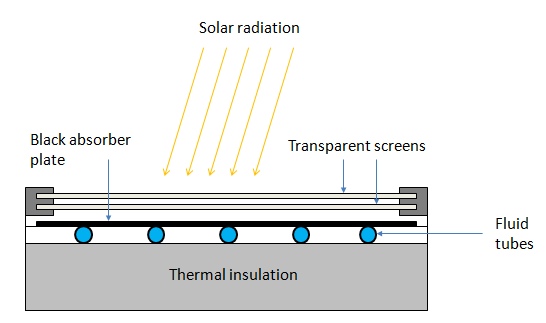
来自 <https://www.e-education.psu.edu/eme811/node/685>
Solar ponds:
In freshwater ponds, the Sun heats the water, and the hot water rises. The water cools through evaporation as the heat is released to the atmosphere, keeping the pond water at atmospheric temperature. Solar pond technology, on the other hand, attempts to prevent the loss of heat from water through the use of salt, the concentration of which increases with depth.
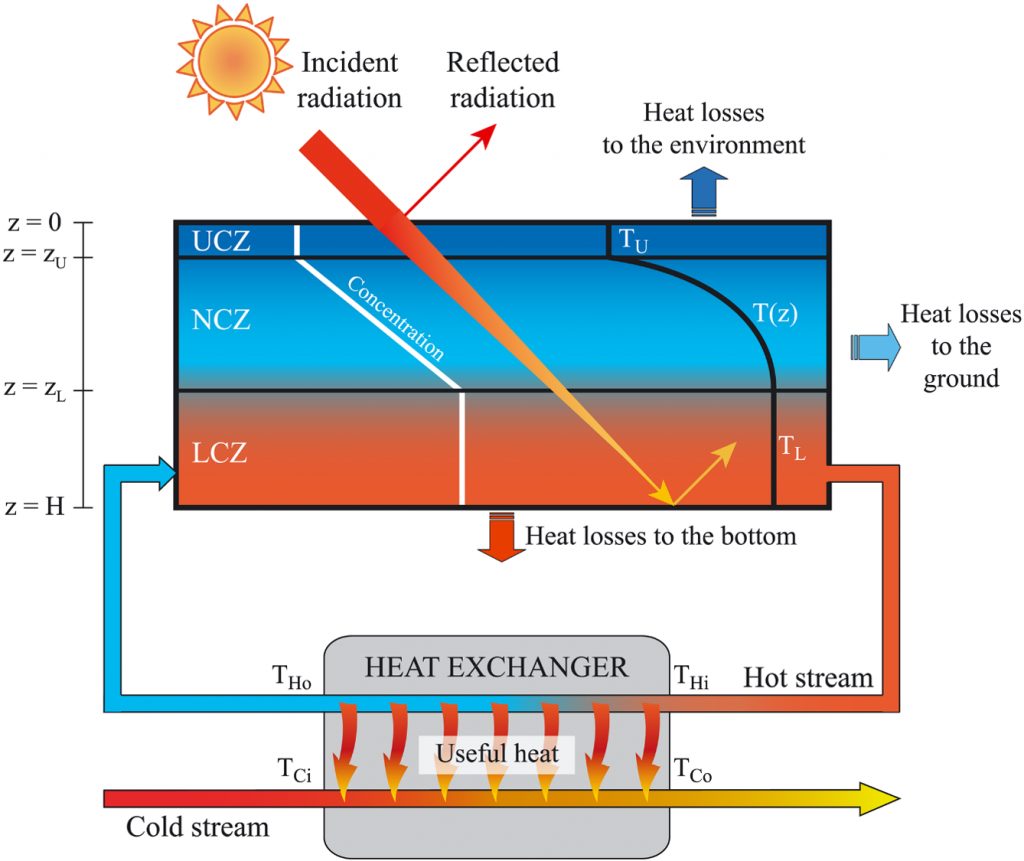
来自 <https://www.britannica.com/technology/solar-pond>
Solar ovens:
Solar oven, also called solar cooker, a device that harnesses sunlight as a source of heat for cooking foodstuffs. The solar oven is a simple, portable, economical, and efficient tool.
来自 <https://www.britannica.com/technology/solar-oven>
Solar cells:
Solar Energy works by converting the sun’s energy into electricity. A solar cell which is also known as photovoltaic (PV) cell converts sunlight into electricity. The process by which voltage is generated in a solar cell is known as “photovoltaic effect”. The photovoltaic effect was first discovered by Edmond Becquerel in 1839.
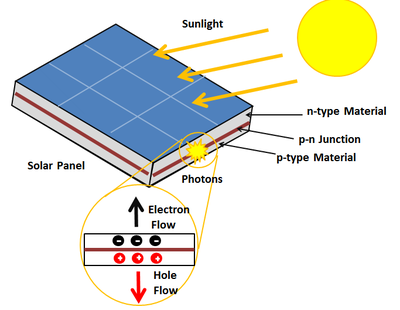
来自 <https://solarpost.in/basics/solar-photovoltaic-effect/>

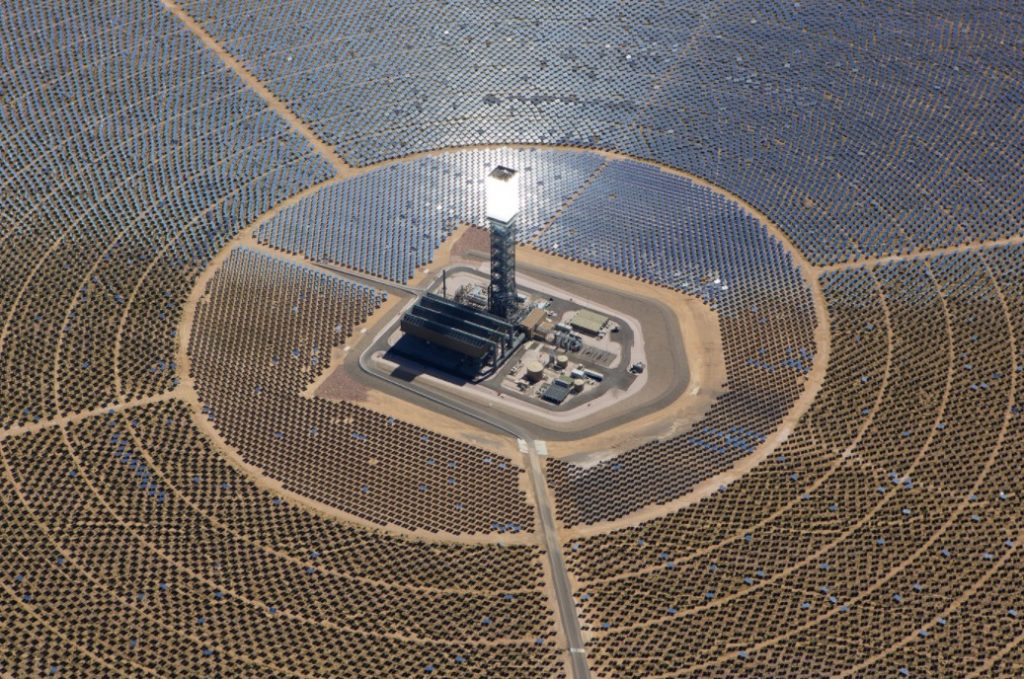
Concentrated solar power plants:
Concentrated solar power systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a receiver. Electricity is generated when the concentrated light is converted to heat, which drives a heat engine connected to an electrical power generator or powers a thermochemical reaction.

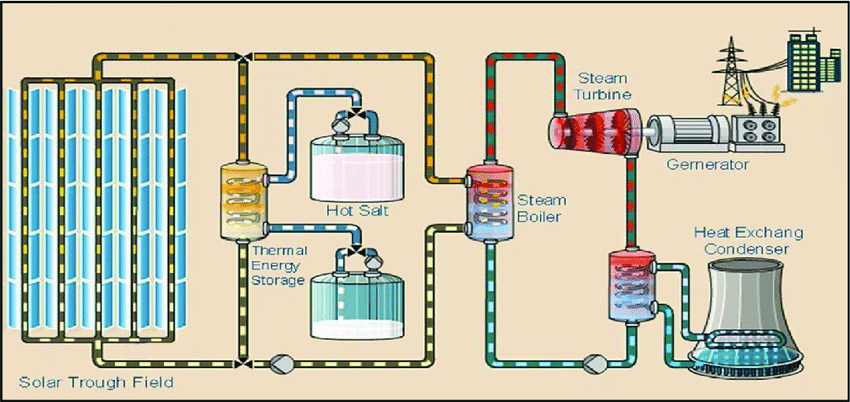
4.Some other ways of using solar energy.
In some countries, for instance, solar energy is used to produce salt from seawater by evaporation. Similarly, solar-powered desalination units transform salt water into drinking water by converting the Sun’s energy to heat, directly or indirectly, to drive the desalination process.
Solar technology has also emerged for the clean and renewable production of hydrogen as an alternative energy source. Mimicking the process of photosynthesis, artificial leaves are silicon-based devices that use solar energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, leaving virtually no pollutants.

留言